The Aorta Is Classified as One of These Vessels
These vessels have thicker walls and a heavier tunica media. The aorta is one of the most important arteries and the largest blood vessel in the human body.

Aortic Dissections About What S Happening
Intima media and adventitia and may progress to rupture or dissection.

. 3 An abdominal aortic. Blood pressure in these vessels is low. Several arteries extend from the aorta to deliver blood to the various regions of the body.
It arises from the left ventricle of the heart and travels superiorly to form the ascending aorta. The aorta classified as a large elastic artery and more information on its internal structure can be found here. The venules and veins returning blood to the heart.
The peripheral vascular system PVS includes all the blood vessels that exist outside the heart. The very first complication of aortic calcification is having a risk of aortic valve stenosis. The aorta rises from the left ventricle of the heart forms an arch then extends down to the abdomen where it branches off into two smaller arteries.
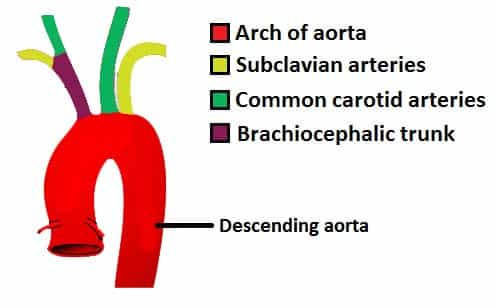
The brachiocephalic artery the left common carotid artery and the left subclavian literally under the clavicle artery. It then loops inferiorly to form the arch of the aorta and through the thorax to form the thoracic aorta. It terminates at the level of L4 by bifurcating into the left and right common iliac arteries.
Calcification of aorta can have serious complications related to it. This final part of the aorta gives rise to the largest number of arteries. The aorta is the main artery of the human body.
Function of the Aorta The aorta carries and distributes oxygen-rich blood to all arteries. The ascending aorta rises up from the heart and is about 2 inches long. The peripheral vascular system is classified as follows.
The aorta is a large cane-shaped vessel that delivers oxygen-rich blood to your body. This part has many smaller arteries branching out from it that supply blood to the esophagus pericardium the top part of the diaphragm lymph nodes ribs and some other structures in the chest. These vessels have thinner walls and transport oxygen-poor blow.
The function and structure of each segment of the peripheral vascular system vary depending on. The thoracic aorta runs from the aortic arch to the diaphragm which is the point of separation between the chest cavity and the abdominal cavity. These entities constitute circumscribed dilations found in arteries characterized by progressive focal dilatation of the vessel wall involving all three layers.
There are three major branches of the aortic arch. The walls of large blood vessels like the aorta and the vena cava are supplied with blood by vasa vasorum. Some of these larger vessels have valves to prevent back flow arteries these vessels carry blood away from the heart arteries the aorta is classified as one of these vessels arteries these vessels have thicker walls and a heavier tunica media capillaries nutrient and gas exchange occur in these vessels capillaries venules drain these tiny vessels.
The aorta is classified as a large elastic artery. Reset Help capillaries The aorta is classified as one of these vessels veins These vessels have thinner walls and transport oxygen-poor blood arteries Blood pressure in these vessels is low or even negative These vessels have thicker walls and a heavier tunica media Some of these larger vessels have valves to prevent backflovw Superior and inferior vena cava are classified as. Arteries of which the aorta is the largest vessel in the human body.
The aorta is classified as one of these vessels. Appointments 8006597822 Appointments Locations Talk to a Heart Nurse. Nutrient and gas exchange occur in these vessels.
The aorta initially is one inch wide in diameter. The aorta and its branches. The arteries branching out from it supply the liver diaphragm.
The type of blood vessel is an arteryThe largest an elastic one connected to the heart is the aorta. 2 They are defined as aneurysm when the vessel diameter is greater than 3 cm or 15-fold its original diameter. The aorta is classified as one of these vessels these vessels carry blood away from the heart these vessels have thicker walls and a heavier tunica media Capillaries Venules drain these tiny vessels nutrient and gas exchange occur in these vessels.
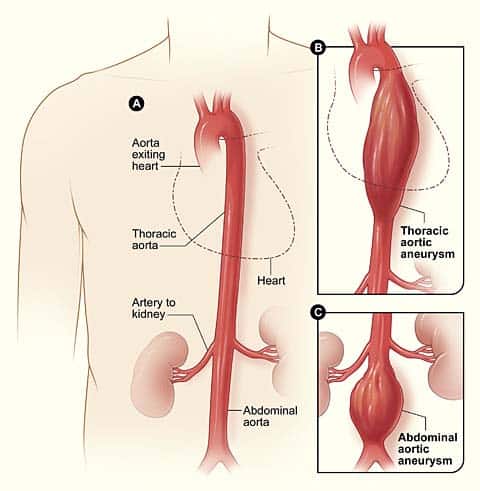
Along the way blood vessels branch off the aorta extending to organs and supporting tissue. THE AORTA The Aorta is the largest artery of the body which carries the oxygenated blood from the left ventricle and supplies it to all the parts of the body. THE AORTA The aorta can be divided into four sections.
Explore the anatomy of the aorta including its. It starts in the lower-left part of the heart and passes through the chest and abdomen. It provides blood to the muscles of the chest wall and the spinal cord.
The patient should be aware of the following issues-. The ascending aorta the aortic arch the thoracic descending aorta and the abdominal aorta. The abdominal aorta runs from the diaphragm and ends just above the pelvis where it divides into the iliac arteries.
The aorta can be divided into four sections. After crossing the diaphragm into the abdomen the aptly-named abdominal aorta eventually bifurcates into the common. The coronary arteries branch off the ascending aorta to supply the heart with.
It blocks the valve due to calcium deposition thereby affecting the flow of blood throughout the body. As you would expect based upon proximity to the heart each of these vessels is classified as an elastic artery. This term translates to mean vessel of a vessel Three types of vasa vasorum exist 1 vasa vasorum internae 2 vasa vasorum externae and.
The aorta is divided into four sections.
The Aorta Branches Aortic Arch Teachmeanatomy

Comments
Post a Comment